Advantages of Welded Bus Duct Enclosures Versus Bolted Enclosures in Power Generation Facilities

In power generation facilities, the reliability and efficiency of electrical bus duct systems is crucial. One of the key considerations is the choice between welded bus duct enclosures and bolted enclosures or shunts. This article explores the advantages of welded enclosures over their bolted counterparts, addressing key factors such as design continuity, water and foreign material intrusion, current flow consistency, and maintenance requirements.

Welded Enclosures: A Superior Solution
1. Continuous Isolated Phase Bus (IPB) Design
Welded enclosures provide a seamless, continuous IPB design that eliminates gaps and weak points where electrical performance could degrade. This uninterrupted configuration ensures uniformity and structural integrity, crucial for high-reliability power generation applications.
2. Mitigation of Water and Foreign Material Intrusion
The continuous design of welded enclosures minimizes entry points for water, dust, and debris. In contrast, bolted enclosures rely on gaskets, which can degrade over time, leading to potential ingress of contaminants. Welded designs offer long-term protection against environmental factors, ensuring system reliability.
3. Establishing a Constant and Continuous Path for Current Flow
Welded connections ensure an uninterrupted current path, which is critical for maintaining stable electrical performance. The absence of bolted joints eliminates variations in electrical contact resistance, resulting in improved system efficiency and reduced energy losses.
4. Mitigation of Circulating Currents, Hot Spots, and Overheating
The seamless nature of welded enclosures eliminates junction points where circulating currents and hot spots often develop. This reduces the risk of localized overheating, enhancing the thermal performance and longevity of the system.
5. Elimination of Gasket Material Maintenance
By removing the need for gaskets entirely, welded enclosures eliminate the associated preventive maintenance (PM) requirements. This reduces operational costs and the risk of failure due to gasket degradation, freeing up resources for other critical maintenance activities.
Bolted Enclosures: Challenges and Limitations
1. Non-Continuous IPB Design
Bolted enclosures inherently lack the continuity of a welded design. Each bolted connection introduces potential weak points that can disrupt the flow of current, reducing system reliability and efficiency.
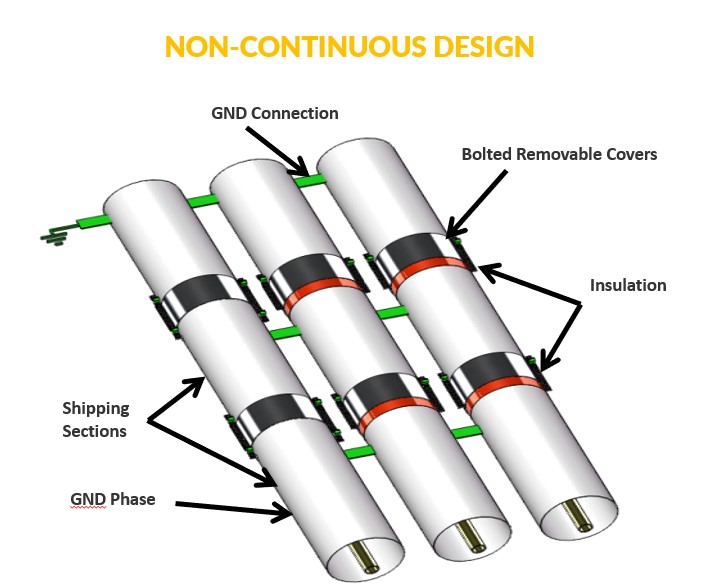
2. Vulnerability to Water and Foreign Material Intrusion
Gasket Material Degradation: Over time, gasket materials in bolted enclosures degrade due to environmental factors, such as temperature fluctuations and UV exposure. This degradation can allow water and foreign materials to enter the enclosure, leading to insulation damage, corrosion, and other operational issues.
Misalignment: Misalignment at bolted connections further exacerbates the risk of water and foreign material intrusion. Improper assembly or shifting during operation can compromise the enclosure’s seal, creating vulnerabilities in the system.
4. Overheating Risks
Bolted connections are prone to overheating due to several factors:
- Improper Torquing Practices: Inconsistent or insufficient torque can affect contact pressure, leading to increased resistance and heat generation.
- Improper Application of Connection Grease: The application of incorrect or insufficient conductive grease at bolted joints can compromise electrical performance.
- Lack of Testing: Regular testing with a Digital Low Resistance Ohmmeter (DLRO) is necessary to ensure optimal contact resistance, yet this step is often overlooked.
- Bolting Hardware Loosening While Under Load: Thermal cycling and vibration during operation can cause bolted hardware to loosen over time, further increasing resistance and the risk of overheating.
5. Increased Maintenance Requirements
Gasket Material Maintenance: Unlike welded enclosures, bolted systems require ongoing preventive maintenance to inspect, repair, or replace gasket materials. This adds to operational costs and increases downtime.
Validation of Bolted Connections: Periodic testing and retorquing of bolted joints are essential to ensure reliable performance, increasing the overall maintenance burden.
Conclusion
Quality welded bus duct enclosures, by properly trained personnel provide a robust, low-maintenance, and highly reliable solution for power generation facilities. Their continuous design eliminates the vulnerabilities associated with bolted enclosures, such as contamination, overheating, and extensive maintenance requirements. While bolted systems may have lower initial costs, the long-term benefits of welded enclosures in terms of reliability, efficiency, and reduced maintenance far outweigh the upfront investment.
By choosing welded enclosures, power generation facilities can ensure improved system performance, lower operational risks, and enhanced longevity, making them the superior choice for critical applications.
